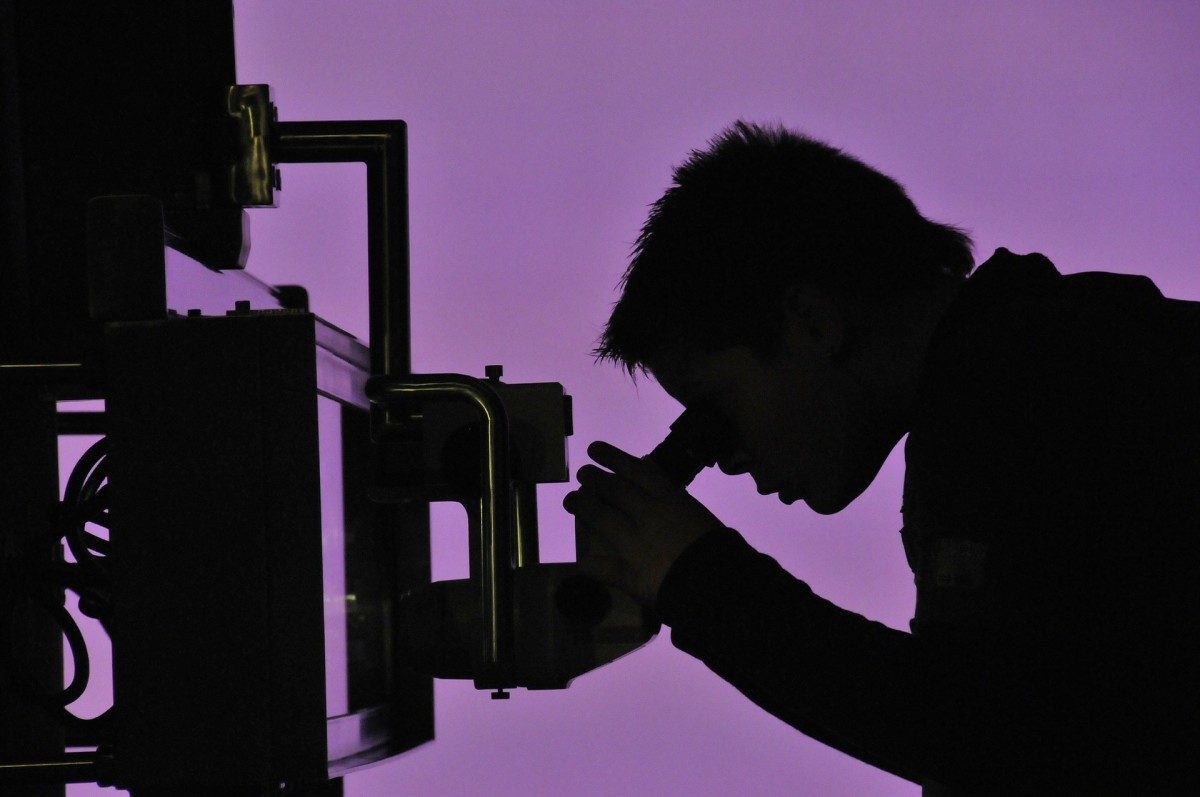
U of M and UWinnipeg collaborate on commercialization of technologies
Inventors at the University of Winnipeg will now have access to the expertise and services of the University of Manitoba’s Technology Transfer Office, under a recently signed service agreement.
“This collaboration to utilize existing services makes sense for all parties,” says Dr. Digvir Jayas, Vice-President (Research and International) and Distinguished Professor at the University of Manitoba. “It prevents duplication by using the existing suite of capabilities available at the University of Manitoba.”
The U of M currently provides similar services to: Brandon University, Winnipeg Regional Health Authority, Health Sciences Centre, St-Boniface General Hospital, Children’s Hospital Research Institute of Manitoba and CancerCare Manitoba.
“This is a great example of how universities and research centres in Manitoba are collaborating to leverage the greatest outcomes possible for the entire province with respect to commercialization of technologies and ideas,” says Dr. Jino Distasio, UWinnipeg’s Vice-President, Research and Innovation. “This gives us a process to take our knowledge out into the community for the benefit of all.”
The services provided include:
- Invention assessment for commercial and technical viability
- Patenting assistance and coordination with patent agents (if required)
- Market assessment and marketing of technology to potential receptors
- Discussion and recommendations on commercialization strategies with inventors
- Assistance in identifying corporate partners and with creation of startup companies (if required)
- License negotiations (if required)
The University’s Transformational Partnerships approach supports the success of Manitoba companies through collaborative research and development partnerships. In 2015-16 the initiative enabled 30 collaborations or requests for funding totaling $8.8 million.
Read more about Transformational Partnerships and the Technology Transfer Office.
Research at the University of Manitoba is partially supported by funding from the Government of Canada Research Support Fund.