Children less infectious than adults infected with COVID-19
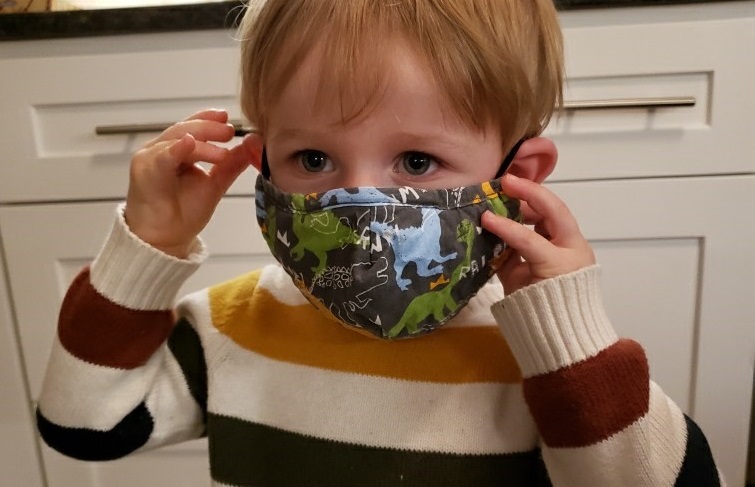
Children may not be as infectious in spreading COVID-19 to others as previously thought, according to new University of Manitoba-led research in CMAJ Canadian Medical Association Journal.
“Our findings have important public health and clinical implications,” writes principal investigator Dr. Jared Bullard, associate professor, pediatrics/child health and medical microbiology/infectious diseases, Max Rady College of Medicine, University of Manitoba and associate medical director, Cadham Provincial Laboratory in Winnipeg, Manitoba. “If younger children are less capable of transmitting infectious viruses, child daycare, in-person school and cautious extracurricular activities may be safe to continue, with appropriate precautions in place, with lower risk to childcare staff, educators and support staff than initially anticipated.”
Fourteen researchers from multiple disciplines at the University of Manitoba, Cadham Provincial Laboratory, Manitoba Health and Seniors Care and the Public Health Agency of Canada’s National Microbiology Laboratory analyzed samples from 175 children and 130 adults in Manitoba infected with COVID-19 to see if there was a difference in infectiousness. Using cell cultures of naso-pharyngeal swabs, they investigated viral loads in both groups to determine if children are more infectious.
“As an increasing number of jurisdictions consider whether in-school learning, daycares and extracurricular activities should continue or resume, a better understanding of the relative contributions of children and adolescents to forward transmission of COVID-19, when compared with adults, is essential,” the authors write. “This is particularly significant as asymptomatic infection is more likely in this group.”
“Infectivity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in children versus adults from nasopharyngeal swab samples diagnostic of coronavirus disease 2019” is published April 9, 2021.