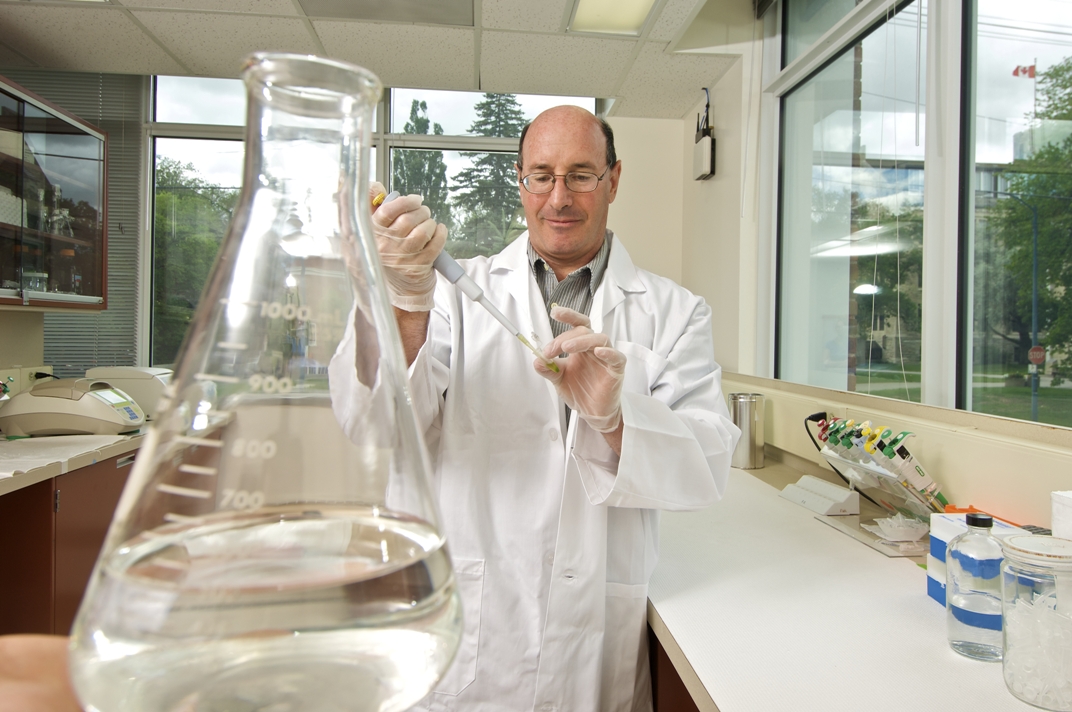
Working on the next big thing
Vision to Venture, bringing money and minds together
A new event takes place in Smartpark on Feb. 1.
Called Transformational Partnerships: Vision to Venture, this event will bring Winnipeg’s top entrepreneurs in contact with the top scientists and product developers who will be showcasing patent-pending technologies awaiting financial investment to get them to market.
When: Feb. 1, 2014, 9 a.m. to 5 p.m.
Where: Event Centre, 100-one Research Road
Technologies on offer
Novel probiotics/prebiotic system for pig health
These are patented and ATCC-registered bacterial strains that protect piglets from K88+ E coli. bacterial infections. These pathogens are a worldwide and common cause of piglet morbitity. The strains were chosen so that they would work best with a potato-starch enhanced diet.
Apparatus for left-sided catheter insertion
Seldinger’s technique is a method of inserting a catheter for direct access to the heart. This is typically inserted on the patient’s right side, however in up to 20 percent of cases, a left sided insertion must be done (such as infection or injury of the right side). In these cases the existing apparatus is of the wrong shape and size. This invention provides an apparatus design specifically for use in these cases. The total market for the existing apparatus is 3.2 million units, or $219 Million.
Novel co-polymer micelles for drug delivery
Polymeric micelles are suited for drug – delivery purposes, particularly fat-soluble and toxic drugs. Micelles also reduce degradation and excretion. Dr. Xing has developed micelle-forming amphipathic compounds that become unstable within cancer cells and tumour tissue – low pH, and high glutathione levels. The compounds form stable, high-volume micelles in blood plasma.
Solid Particle Seed Generator
Measurement of fluid dynamics characteristics often require the use of non-intrusive laser-based techniques, such as particle image velocimetry (PIV) and laser Doppler velocimetry (LDV). These techniques require “seeding” the fluid with micro-sized particles. These particles, which act as tracing material for the fluid motion, must have proper size and concentration/density in a flow field. Tracers should also be distributed uniformly and supplied steadily.
Current solid particle seeders have known limitations especially in low flow applications. The new U of M design overcomes these limitations by utilizing a horizontal seeder in which the particles are agitated using a rotating brush. Particle concentration in the flow is controlled by simply varying the speed of rotation. Further, particle agglomeration is avoided by implementing a unique sonic valve.
Low-Cost Portable Microfluidic System for Cell Migration Studies
Summary of Technology: Toward providing a full practical solution for performing microfluidic cell migration analysis in an integrated manner, the inventors have developed a prototype USB microscope-based Microfluidic Chemotaxis Analysis System (“UMCAS”). The UMCAS integrates a microfluidic device, gradient and cell imaging, temperature control, and real-time data analysis to provide a low cost and portable solution for rapid microfluidic cell migration and chemotaxis experiments. Furthermore, a smartphone-based module was developed for remote experiment data monitoring.
Systems and Methods for Detecting Corrosion of Steel Reinforcement
An embedded coupled coil sensor able to monitor the corrosion potential of reinforcement steel in concrete is presented. The sensor is based on coil resonator whose resonant frequency changes with an applied voltage. The sensor state can be monitored externally by a coupled coil. An accelerated corrosion test shows that it can provide useful information about the corrosion state and the level of chloride ingress into the concrete. The wireless sensor is passive and simple in design, making it an inexpensive, batteryless option for remote long-term monitoring of the corrosion state of reinforcing steel.
SmartColor: User-Interface Components for Head-Worn Displays
One major usability issue of Head-Worn Displays is that light coming from real-world objects mixes with the light emitted by the display, resulting on a different color. This problem, also known as color blending, is an important issue which affects the legibility and color coding of digital content, compromising the general usability of head-worn devices. Color blending is an outstanding issue of existing and upcoming transparent technologies, and its importance has been highlighted in several usability studies.
We present the SmartColor middle-ware, a software layer that counters the negative effects of color-blending and supports new types of user-interface components. By using an embedded camera to estimate color-blending at a pixel level, SmartColor components can be 1) color corrected, 2) contrast preserved, or 3) conditionally shown; all in real time.
Research at the University of Manitoba is partially supported by funding from the Government of Canada Research Support Fund.